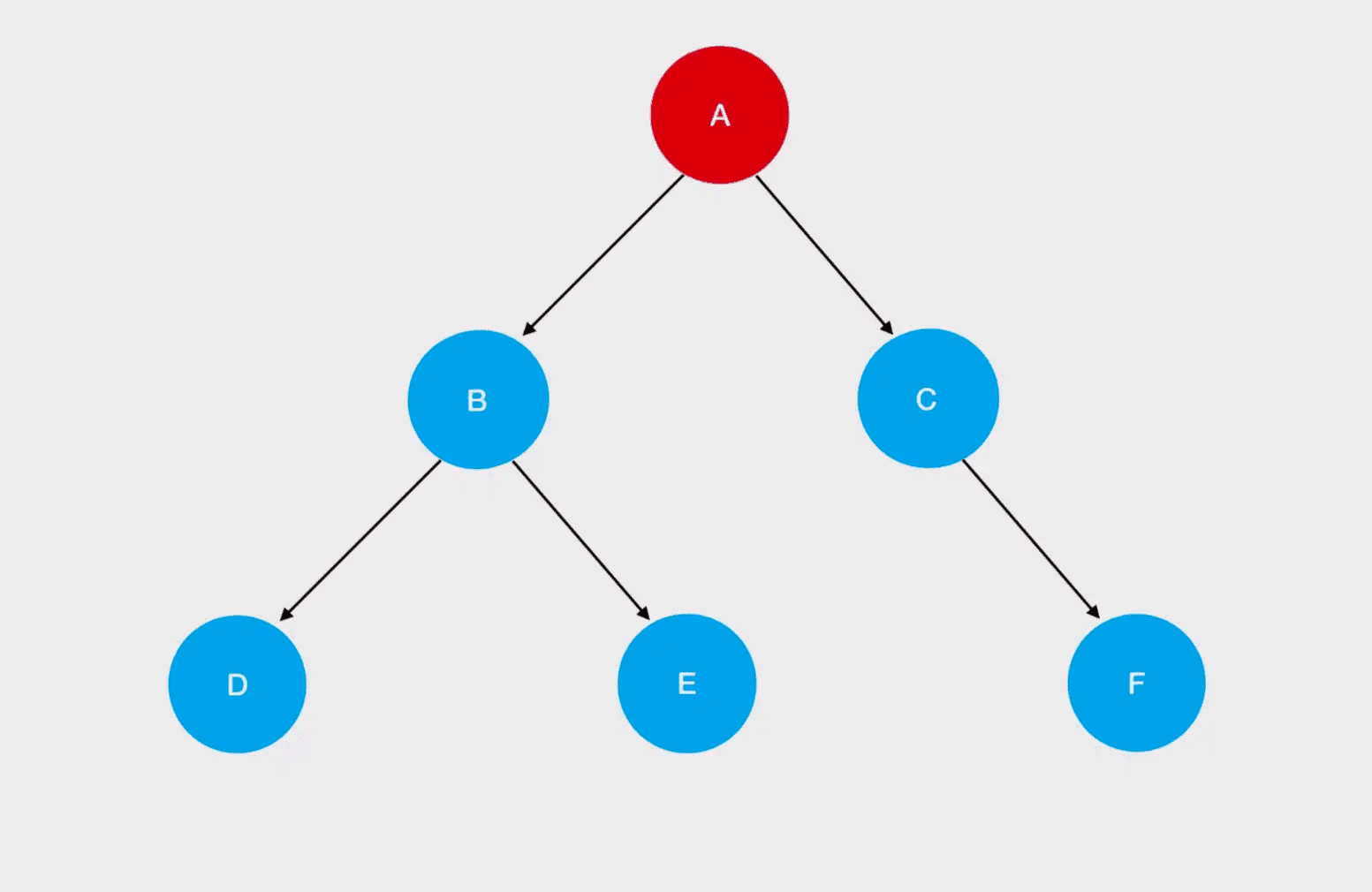
javascript
const root = {
val: 'A',
left: {
val: 'B',
left: {
val: 'D'
},
right: {
val: 'E'
}
},
right: {
val: 'C',
right: {
val: 'F'
}
}
}根据根节点便利的时机实现
前序遍历
javascript
function preOrder(root) {
if(!root) {
return
}
console.log('当前遍历的节点是:', root.val);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}中序遍历
javascript
function inOrder(root) {
if(!root) {
return
}
inOrder(root.left);
console.log('当前遍历的节点是:', root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}后序遍历
javascript
function lastOrder(root) {
if(!root) {
return
}
lastOrder(root.left);
lastOrder(root.right);
console.log('当前遍历的节点是:', root.val);
}下面使用迭代的方式来解决
中序遍历
先遍历到左子树 遍历时将子树依次入栈方便后续作为根节点来获取 val
javascript
const inorderTraversal = (root) => {
const res = [];
const stack = [];
let cur = root;
while(cur || stack.length) {
while(cur) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
res.push(cur.val);
cur = cur.right
}
return res;
}层序遍历
根据二叉树 1-> 2->4 的规律依次入栈取值存储后得出
javascript
const levelOrder = (root) => {
const res = [];
if(!root) return res;
const queue = [];
queue.push(root);
while(queue.length) {
const level = [];
const len = queue.length
for(let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const cur = queue.shift();
console.log(level, cur.val, queue.length);
level.push(cur.val);
if(cur.left) {
queue.push(cur.left)
}
if(cur.right) {
queue.push(cur.right);
}
}
res.push(level);
}
return res;
}反转二叉树
javascript
const invertTree = (root) => {
if(!root) return root;
const left = invertTree(root.left);
const right = invertTree(root.right);
[root.left, root.right] = [right, left];
return root;
}